
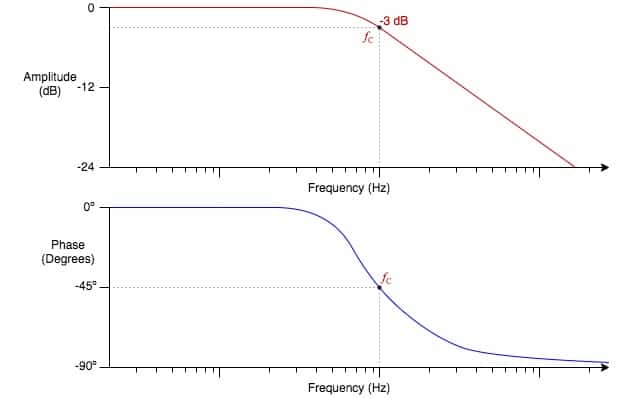
Parametric or paragraphic EQs allow you to control all three of these parameters (frequency, gain, Q) independently, while semi-parametric EQs use fixed settings for some of the parameters. Q is also applied to shelves and filters, and dictates how steep of a curve their adjustments come into play along the frequency spectrum. Low Q values affect a wider range of frequencies and tend to sound more gentle when used subtly. High Q values use steeper curves, which affect a smaller range and allow you to pinpoint specific frequencies. The Q parameter stands for quality, and controls the shape of the EQ curve. Turning the gain up increases the amount of the frequency to add, and turning the gain down removes more of that frequency. Gain controls how much of the selected frequency is added or removed. Filters are used to cut all the way to zero, or remove everything below (a high-pass filter) or above a certain point (a low-pass filter), which means either way, they're inherently subtractive. Shelves are used to boost or attenuate everything below (low-shelf) or above a certain point (high-shelf). Bells allow you to boost or cut, and are designed to focus on a specific frequency. Parametric EQs also allow you to choose between three basic EQ shapes: bells, shelves, and high-pass / low-pass filters.Ī bell curve uses the selected frequency as the center point for its boosting or cutting, whereas shelves and HP / LP filters use their selected frequencies as the starting point for their adjustments. The human hearing range runs from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, so most EQs allow you to select frequencies within that range. The frequency control allows you to select which frequency you want to manipulate. It takes years of practice to fully understand the capabilities of an equalizer, but it all boils down to three controls: The first step is to develop an understanding of how an equalizer works.Īs simple as it may seem, the art of equalization is not an easy one to learn. Both methods have their benefits, but it can be difficult to know when to use which approach. The act of cutting or attenuating a frequency is known as subtractive EQ.
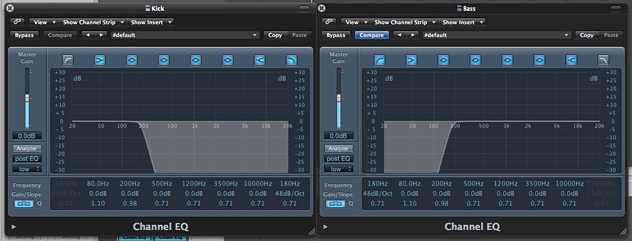
The act of boosting or adding more of a frequency range is called additive EQ. Surprisingly, these sophisticated tools only have two functions: to add more of, or to reduce the amount of a set of frequencies.
It can repair a poor recording, or transform the sound of an instrument. additive EQ parameters for your mix.Įqualization is a mixing engineer's most powerful tool.


We’ve all heard “Cut, don’t boost!” But is that true? How do you know if you should boost or cut when sculpting EQ? Learn when to do each, and how to set the most effective subtractive vs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
